English
English-
 English
English -
 Español
Español -
 Português
Português -
 русский
русский -
 Français
Français -
 日本語
日本語 -
 Deutsch
Deutsch -
 tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt -
 Italiano
Italiano -
 Nederlands
Nederlands -
 Polski
Polski -
 한국어
한국어 -
 Svenska
Svenska -
 magyar
magyar -
 Malay
Malay -
 বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার -
 Dansk
Dansk -
 Suomi
Suomi -
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी -
 Pilipino
Pilipino -
 Türkçe
Türkçe -
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge -
 العربية
العربية -
 Indonesia
Indonesia -
 Norsk
Norsk -
 تمل
تمل -
 český
český -
 ελληνικά
ελληνικά -
 український
український -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 فارسی
فارسی -
 தமிழ்
தமிழ் -
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు -
 नेपाली
नेपाली -
 Burmese
Burmese -
 български
български -
 ລາວ
ລາວ -
 Latine
Latine -
 Қазақша
Қазақша -
 Euskal
Euskal -
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan -
 Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk -
 Македонски
Македонски -
 Lietuvos
Lietuvos -
 Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel -
 Română
Română -
 Slovenski
Slovenski -
 मराठी
मराठी -
 Srpski језик
Srpski језик -
 Yoruba
Yoruba
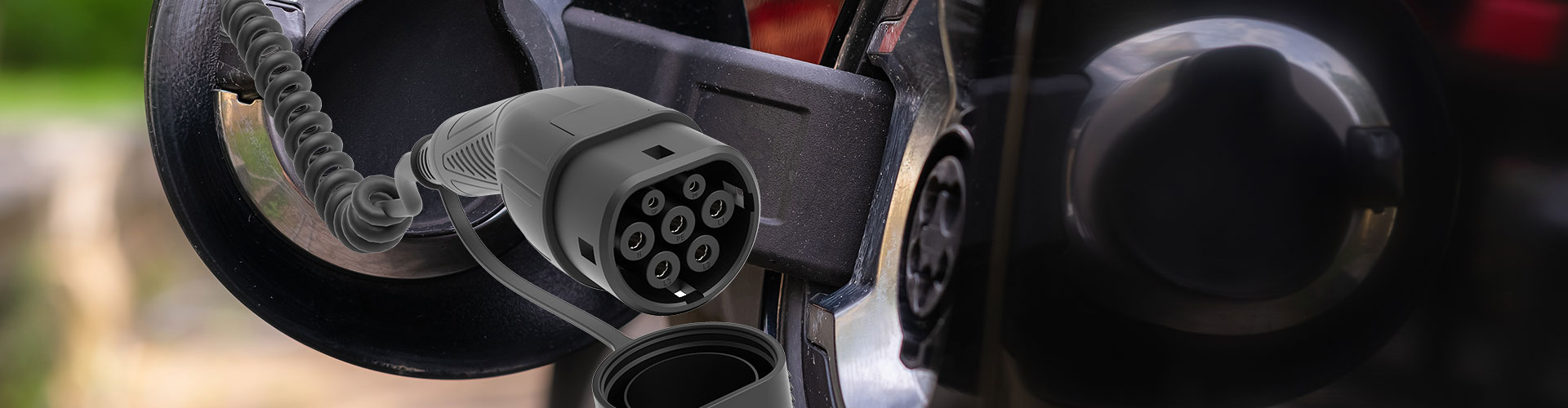
What is charging infrastructure?
2024-11-21
Charging infrastructure refers to the network of equipment and facilities that support the charging of electric vehicles (EVs). This includes charging stations, charging points, and the associated hardware and software required to deliver power to EVs.
Here are the key components and characteristics of charging infrastructure:
Charging Stations and Points: These are the physical locations where EVs can be charged. Charging stations can range from simple wall-mounted chargers to more complex, high-power DC fast-charging stations. Charging points, on the other hand, refer to individual units within a charging station that provide power to EVs.
Power Delivery: Charging infrastructure uses various power levels and technologies to deliver electricity to EVs. Level 1 charging, for example, uses a standard household outlet and provides a low rate of charge. Level 2 charging uses a dedicated 240-volt circuit and can charge an EV more quickly. DC fast-charging stations, on the other hand, use high-power direct current to rapidly recharge EV batteries.
Network Connectivity: Many charging stations are connected to a network that allows for remote monitoring, management, and payment processing. This connectivity also enables EV drivers to find and use charging stations through mobile apps and online platforms.
Interoperability: Charging infrastructure is designed to be interoperable, meaning that EVs from different manufacturers can use the same charging stations and points. This ensures that EV drivers have access to a wide range of charging options regardless of their vehicle's make or model.
Scalability: Charging infrastructure is scalable and can be expanded to meet the growing demand for EV charging. This includes adding more charging stations and points, upgrading existing equipment, and integrating new technologies to improve charging speeds and efficiency.
Charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of EVs and is a key component of the transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon transportation system. Governments, private companies, and other stakeholders are investing in the development and expansion of charging infrastructure to support the growing number of EV drivers.